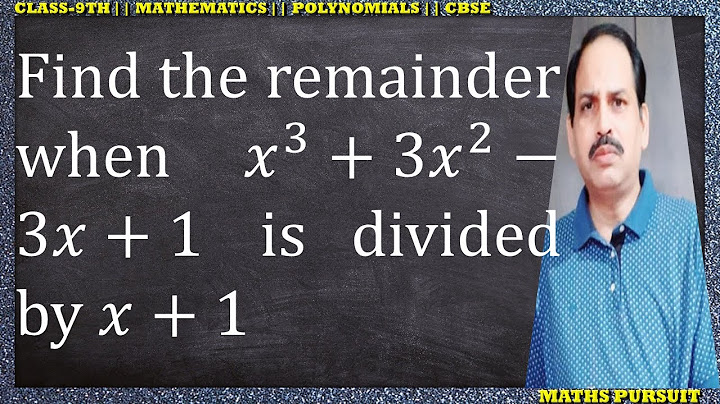Show How do you solve factor and remainder theorem?The Factor and Remainder Theorems
If p(x) is a polynomial of degree 1 or greater and c is a real number, then when p(x) is divided by x−c, the remainder is p(c). If x−c is a factor of the polynomial p, then p(x)=(x−c)q(x) for some polynomial q. Then p(c)=(c−c)q(c)=0, showing c is a zero of the polynomial.
What is remainder and factor theorem Class 9?Remainder Theorem Definition
Problems are solved based on the application of synthetic division and then to check for a zero remainder. When p(x) = 0 then y-x is a factor of the polynomial Or if we consider the other way, then When y-x is a factor of the polynomial then p(x) =0. Read more: Long division of Polynomial.
What is the remainder theorem example?Example: 2x2−5x−1 divided by x−3
After dividing we get the answer 2x+1, but there is a remainder of 2. Say we divide by a polynomial of degree 1 (such as "x−3") the remainder will have degree 0 (in other words a constant, like "4").
What is remainder theorem Class 9 formula?Let g(x) be a polynomial of degree 1 or greater than 1 and let b be any real number. If g(x) is divided by the linear polynomial x – b, then the remainder is p(b).
|

Advertising
LATEST NEWS
Advertising
Populer
Advertising
About

Copyright © 2024 moicapnhap Inc.